Home > Animals
Aquaponics- PDF eBook
Look Inside
The Aquaponics ebook will give you a great understanding of how to start your own aquaponics production. This 65 page ebook provides you with enough information to start your own home production and even manage issues as they arise. This is a great way to become more self-sufficient and produce a sustainable food source for your own household.
Aquaponic farming allows individual families to grow a much wider range of produce, in a much smaller space. They can provide the protein needed for their diet (from fish), as well as the vegetables and fruit they need. Aquaponic systems can be as small as a few cubic meters; or as large as many acres. They are an ideal way of improving productivity on a hobby farm; can be used by restaurants to produce the freshest produce on site, or established inside buildings, in big cities, for urban farming.
ISBN: 978-0-9925878-6-4
Pages: 65
Images: 40
Table of Contents
CREDITS
PREFACE
CHAPTER 1 SCOPE AND NATURE OF AQUAPONICS
What grows well in aquaponics?
Home systems
Commercial farms
Advantages of aquaponics
Aquaponics is about balance
CHAPTER 2 THE AQUAPONICS SYSTEM
What media is best for your grow beds?
What else do you need to consider?
CHAPTER 3 GROWING FISH IN AQUAPONICS
Key facts for growing fish in aquaponics
Feeding fish
How many fish?
Monitoring fish
Common problems and their symptoms
CHAPTER 4 FISH SUITED TO AQUAPONICS
Silver Perch (Bidyanus bidyanus)
Golden Perch (Macquaria ambigua)
Jade Perch (Scortum barcoo)
Murray Cod (Maccullochella peelii peelii)
Barramundi (Lates calcrifera)
Brown Trout (Salmo trutta)
Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Carp
Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio)
Catfish
Eel Tailed Catfish (Tandanus tandanus)
Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus)
Silver Cobbler (Neoarius midgleyi)
Lake Argyle Catfish (syn. Arius midgleyi)
Eels (Anguilla)
Tilapia
Freshwater Crayfish
Marron (Cherax tenuimanus)
Red Claw (Cherax quadricarinatus)
Yabbies (Charax destructor)
CHAPTER 5 GROWING PLANTS IN AQUAPONICS
What system?
Planting guide
Planting
Herbs
Some herbs to grow hydroponically
Basil (Sweet) (Ocimum basilicum)
Mint (Mentha spp.)
Parsley (Petroselinum crispum)
Vegetables
Cabbage (Brassica oleraceae capitata Group)
Lettuce (Lactuca sativa)
Pak-choi and Bok-choy (Brassica rapa - pekinensis Group)
Spinach (Spinacia oleracea)
Other
Iris Species (Iris spp.)
Nutrients and deficiencies
Mobile and immobile nutrients
Plant nutrition
Nutrient deficiency
Control of water quality
Measuring pH and EC
EC Meters and EC Controllers
pH Controller
Plant pest and disease problems in aquaponics
Pests
Diseases
Damping-off disease
Grey mould
Powdery mildew
Wilt
APPENDIX
AQUAPONICS CAN BE SMALL OR LARGE
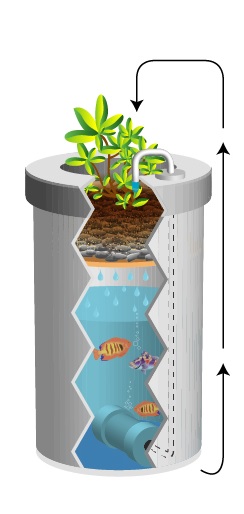 It's possible to do aquaponics on a balcony in as little as 1 square metre. It is also feasible to operate commercial aquaponic farms covering a few or many acres.
It's possible to do aquaponics on a balcony in as little as 1 square metre. It is also feasible to operate commercial aquaponic farms covering a few or many acres.
Home Systems
Although a relatively recent idea, home aquaponics is becoming increasingly realistic for the home garden. Systems can be small enough to fit in even a small courtyard, or large enough to fill any amount of space you have available.
Aquaponics systems are usually made up of grow beds (similar to a corrugated iron raised garden bed), a water pump, an air pump and a filtration system. You can now buy everything you need to get started; kits are readily available and these vary from very simple and inexpensive to quite complex and costly. Before you jump in at the deep end and go for an expensive system it may be best to start small and then add on to the system as your experience and confidence increases. All types of aquaponics kits are now readily available online – try a quick google search.
If you like the idea of aquaponics but are not interested in eating the fish - aquaponic grow beds for plants can be hooked up to existing ornamental fish ponds, as goldfish and other `non-edible’ fish species, work just as well as sources of organic plant nutrients, as edible species.
A very basic aquaponic system simply composed of a fish tank, a filter bed or growbed (for the conversion of nutrients and wastes, as well as a growbed media, a stand, a water pump and a couple of PVC tubes and bell siphons assembled accordingly.
The minimum area required to carry out this basic system should be of at least 1.5 square metres - this way it will be possible to move around the system as well as to provide a reasonable space for adequate plant growth and development.
A sturdy plastic fish tank should be placed partially underneath the stand, over which will rest the grow-bed container. The pump placed inside the fish tank provides two functions:
It firstly serves to aerate the water in the fish tank, along with the assembled PVC tubes and valves. And secondly it carries the nutrient rich water from the fish tank into the growbed. A drainage system by another set of assembled and fitted PVC tubes and siphons will also be necessary for the recirculation of water from the filtering gravel grow bed setup (plants/vegetables) back to the fish tank.
Commercial Farms
Being very intensive - you may not need more than a few acres to contain a commercially profitable aquaponic farm. The costs associated with setting up and running an aquaponic farm can be significantly higher than other forms of farming though. Typically, you can save money on your land purchase, but what you save may then need to be invested in materials, equipment and construction.
Write a Review
Please ensure you are logged in to write a review.
Aquaponics- PDF eBook

£19.95
In stock